Posters for INI2021
1b – Responsible consumption and production and feedbacks in the N cycle
Physiological Nitrogen release
Per capita N footprint in various regions differs and strongly related to protein consumption rates and food production N losses (Galloway et al.,2014). It is essential that in regionswith sanitation facilities...
2a. Livestock production and nitrogen Balance and nutrient cycle
P budget calculations of German farmland
The livestock sector in Germany is characterized by regionally specialized managing systems. Livestock and further the biogasproduction is concentrated in the northwest and the south eastregions, resulting in locally...
Assessment of nitrogen
Priority environmental concerns in livestock and poultry farming in Leningrad Region in manure utilization on large-scale agricultural enterprises. The nitrogen flow on large-scale livestock enterprises in Leningrad...
2a. Livestock production and nitrogen emissions
Identifying cost-effective mitigation strategies for greenhouse gas and ammonia emissions
Collate direct and indirect GHG emissions associated with manuremanagement in livestock production into a single, on-line database. Generate functional relationships between emissions and activity variables....
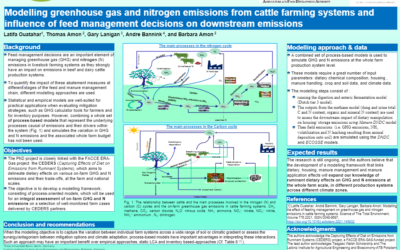
Modelling greenhouse gas and nitrogen emissions from cattle
Feed management decisions are an important element of managing greenhouse gas (GHG) and nitrogen(N) emissions in livestock farming systems as they strongly have an impact on emissions in beef and dairy cattle...
2b. Optimizing the efficiency of nitrogen use in crop production
Nitrogen value of prunnings of Leucaena leucocephala (Lam.) deWit, Senna siamea (Lam.) Irwin & Barneby and Enterolopium cyclocarpum (Jacq.) Griseb.
Increasing pressure on land has led to development of many farming techniques for improved crop prooduction and yield. Plant prunning, an organic source of nitrogen for plant growth (Mund et al. 2016) has ben...
Comparing yield, nutritional quality, water and nitrogen use efficiencies of deficit drip and flood irrigated sorghum
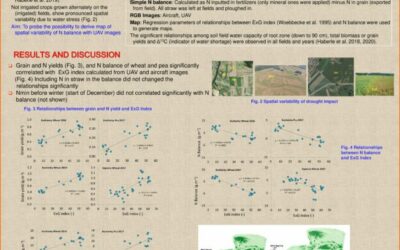
Results showed that crop and irrigation treatments had an effect on yield and water use efficiency (WUE) (Figs 3, 4). The sorghum had significantly higher yields than corn for the treatments at p = 0.05 (Tables 1, 2)...
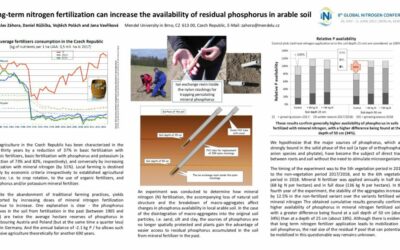
Long-term nitrogen fertilization can increase the availability of residual phosphorus in arable soil
The agriculture in the Czech Republic has been characterized in the past thirty years by a reduction of 37% in basic fertilization with organic fertilizers, basic fertilization with phosphorus and potassium (a...
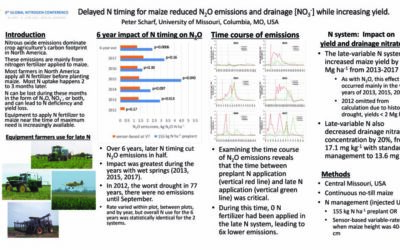
Delayed N timing for maize reduced N2O emissions and drainage
Nitrous oxide emissions dominatecrop agriculture’s carbon footprintin North America. These emissions are mainly fromnitrogen fertilizer applied to maize.
Exploring the Impact of Nitrogen Sources on Yield
Nitrogen (N) constitutes 90% of the applied mineral fertilizers to boost crop productivity. In sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) N inputs are as low as 10 kg N ha-1. The low N inputs have led to depletion of soil...
Wheat productivity at various N-levels and future predictions under changing climate
Nitrogen (N) application to agricultural land has increasedsteeply in recent decades. Pakistan was among the top four in terms of N use but had lowmean yields, with the lowest NUE and highest N surplus. ...
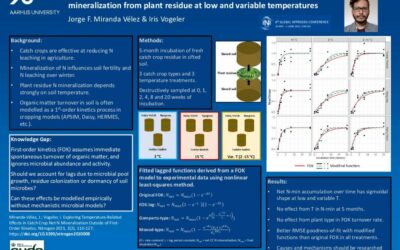
Exploring the limitations of first-order kinetics (FOK) in modelling net N
Catch crops are effective at reducing N leaching in agriculture. • Mineralization of N influences soil fertility and N leaching over winter. • Plant residue N mineralization depends strongly on soil temperature. ...
Indices of crop water stress from uav images
Nitrate concentration has been increasing in water extracted by bore wells in lower Jizera catchment – waterworks Káraný (Fig.1), providing 1/3 of drinking water for Prague. Irrigated vegetables and potatoes,...
Nitrogen and water use efficiency of maize
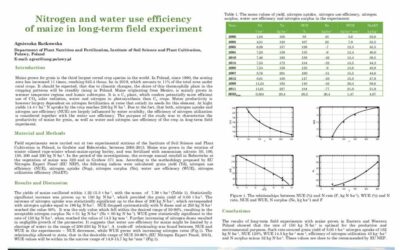
Maize grown for grain is the third largest cereal crop species in the world. In Poland, since 1990, the sowing area has increased 11 times, reaching 645..4 thous. ha in 2019, which acounts to 11% of the total...
Algae extracts as a sustainable nitrogen-containing fertilizer
Nitrogen shortage and loss is a severe global problem. The application of algal biomass/extracts on soil can recover N nutrient. Spirulina platensis treated with subcritical water. .
Urease inhibitor still active at low concentration
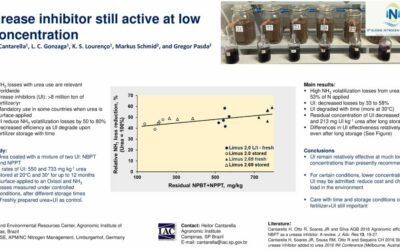
NH3 losses with urea use are relevant worldwide Urease inhibitors (UI): >8 million ton of fertilizer/yr Mandatory use in some countries when urea is surface-applied. UI reduce NH3volatilization losses...
Effect of urease
The rising world population and renewable energy policies are increasing oilseed demand. However, the formation and emission of nitrous oxide (N2O), both directly and indirectly (e.g. derived from ammonia (NH 3)...
Nitrogen use efficiency of maize and cotton
Large farming companies are increasingly concerned with environmental indicators because of the external marked. Need to monitor farming practices. Study: Data from 2011 to 2019 of 4,519 commercial fields (1.32 Mha)...
Changes in nitrogen agricultural practices
Nitrogen (N) is a key indispensable nutrient for all living organisms including humans. For over one century, synthetic fertilizers and agriculture intensification allowed to feed the world population, but this came...
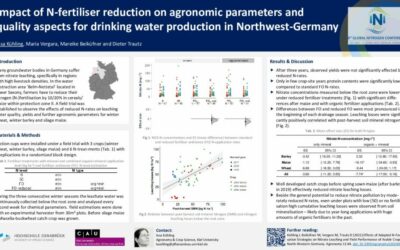
Impact of N-fertiliser reduction
Many groundwater bodies in Germany sufferfrom nitrate leaching, specifically in regionswith high livestock densities. In the waterabstraction area 'Belm-Nettetal' located in Lower Saxony, farmers have to reduce...
2b. Nitrifications & inhibitors; microbes
Root system architecture variability and nitrate reductase activity in wheat
Pakistan is a developing country with high population growth rate. Overuses synthetic fertilizers to produce more food is detrimental to environment. Pakistan ranks 4 th in terms of nitrogen input, for wheat in 2014...
Effect of nitrification inhibitors and soil pH on N2O emissions
Agricultural soils are becoming acidic worldwide in intensive farming systems due to highapplication rates of N fertilizers. This acidification is a major agricultural problem since limits several crops yield. ...
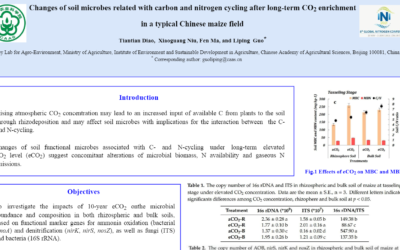
Changes of soil microbes related with carbon and nitrogen cycling
Rising atmospheric CO2 concentration may lead to an increased input of available C from plants to the soil through rhizodeposition and may affect soil microbes with implications for the interaction between the C- and...
1,2,3-Triazoles as Nitrification Inhibitors for Australian Soils
Nitrification is the multi-step oxidation of ammonium (NH4 +) to nitrate (NO3-). Nitrification inhibitors (NIs) can be used to reduce nitrogen losses from synthetic fertiliser application, by slowing the microbial...
3b. Reduction of nitrogen in wastewater to ensure clean water and sanitation
Assessment of the efficiency of nitrogen removal from municipal wastewater
One of the biggest risks to surface waters is the deterioration of their quality as a result eutrophication. The main reason for eutrophication of waters is the local increase in population density, the increasing...
4a. Threats for Biodiversity
Effects of available nitrogen on numbers of native herbaceous plants in Aomori, Japan
Many herbaceous plants are threatened with extinction due to decrease in grassland in Japan. The communities dominated by native herbaceous plants were mostly in soils with low available phosphate in notrthern Kanto...
4b. Threats for aquat. Biodiversity
Nitrate Leaching Potential for Drip Irrigated Cauliflower
• Nitrate (NO3) contamination of groundwater is a significant unresolved environmental issue worldwide. Any Nitrogen (N) fertilizers not taken up by shallow rooted vegetable crops with high demand for N, such as...
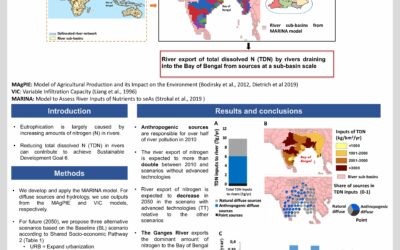
Reducing future nitrogen pollution in rivers
Anthropogenic sources are responsible for over half of river pollution in 2010: Eutrophication is largely caused by increasing amounts of nitrogen (N) in rivers. Reducing total dissolved N (TDN) in rivers can...
Nitrate accumulation in an intensive small agricultural catchment
The long term application of nitrogen (N) fertilizer has changed theglobal N biogeochemical cycle. Understanding the fate of Nfertilizer in soil and plant system (crop uptake, residual in soil, and loss) is important...
Historical N load from land to East-China sea and riverine N2O emission in East-Asia
East-Asia is known to be a hotspot of reactive N (Nr) pollution and hence to be a biggest source of atmospheric N2O among the global regions. In the last halfcentury, the use of N fertilizer in this region was rapidly...
Context is everything: what controls nitrogen concentrations in U.S. streams
Understanding the controls on nutrient concentrations is important for managing aquaticecosystems. Our work focuses on understanding the biologically important summer Nconcentrations of rivers and streams across the...
Nutrient enrichment changes water transport structures
In tropical ecosystems nitrogen availability can affect the use of phosphorus by plants. The second-largest biome of South America, Cerrado, already lost more than 50% to expand croplands and pasturelands.
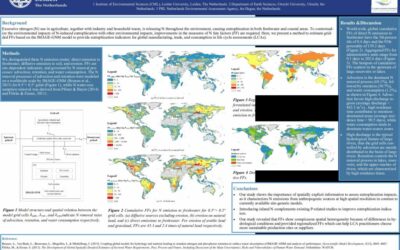
Regionalized nitrogen fate in freshwater systems on a global scale
Excessive nitrogen (N) use in agriculture, together with industry and household waste, is releasing N throughout the environment, causing eutrophication in both freshwater and coastal areas. To contextual-ize...
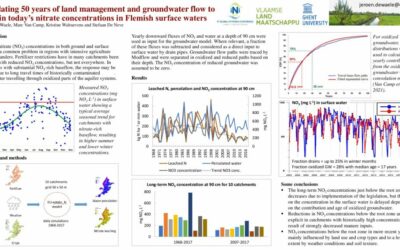
Simulating 50 years of land management and groundwater flow
Elevated nitrate (NO3) concentrations in both ground and surface water are a common problem in regions with intensive agriculture such as Flanders. Fertilizer restrictions have in many catchments been awarded...
5b. Biogeochemical N Cycle
Hydrological N export from tropical forests in the Congo Basin
Nitrogen (N) budgets in tropical African forests show higher N inputs than outputs, however forests paradoxically appear to tightly cycle soil N. We try to compare the magnitude and seasonality of aquatic N export from...
National Nitrogen Budget for Germany
Objectives – Key questions▪ National Nitrogen Budgets (NNB) aims to quantify sources and fate of reactive nitrogen (Nr).▪ How much Nr is introduced into the nitrogen cycle eachyear in Germany?▪ Where does this Nr come...
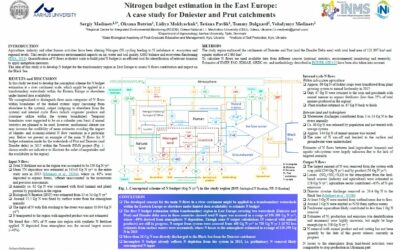
Nitrogen budget estimation in the East Europe: A case study for Dniester and Prut catchments
Agriculture, industry and other human activities have been altering Nitrogen ( cycling leading to N imbalance at ecosystem and regional levels. This results at numerous environmental impacts on air, water and soil...
Assessment of Nitrogen and Carbon compounds emission as aftermath of wildfires in Dniester Delta
Reed-beds and aquatic plants are among main nitrogen (N) and carbon (C) depots in the Dniester Delta capable to accumulate up to 10-15% of N from total annual riverine discharge. No assessment of N and C gaseous...
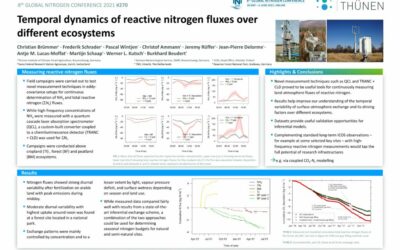
Temporal dynamics of reactive nitrogen fluxes over different ecosystems
Field campaigns were carried out to test novel measurement techniques in eddycovariance setups for continuous determination of NH3 and total reactive nitrogen fluxes. While high-frequency concentrations of NH3...
The potential of ryegrass as cover crop to reduce soil N2O emissions
In terrestrial ecosystems, nitrogen (N) fertilization of agricultural soils is themajor source of nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions. Most of previous incubationexperiments did not include plants and, therefore,...
Variability of atmospheric ammonia and its sources over Indian region
The Indo-Gangetic Plains (IGP) in India is one of the largest NH3 emission hotspots of the world. Atmospheric NH3 is challenging to measure because of its high reactivity, solubility, and its stickiness to the...
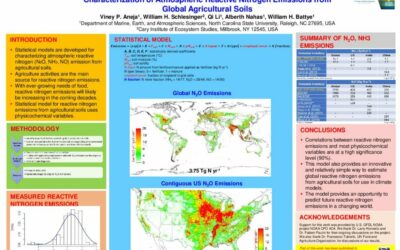
Characterization of Atmospheric Reactive Nitrogen Emissions from Global Agricultural Soils
Statistical models are developed forcharacterizing atmospheric reactivenitrogen (N2O, NH3, NO) emission from agricultural soils. Agriculture activities are the mainsource for reactive nitrogen emissions. ...
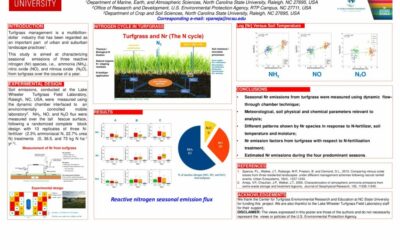
Characterization of Reactive Nitrogen Emissions from Turfgrass
Turfgrass management is a multibillion-dollar industry that has been regarded as an important part of urban and suburban landscape practices1. This study is aimed at characterizing seasonal emissions of three...
Reactive Nitrogen Flows Between Sector Energy and Transport and the Atmosphere
The Convention on Long-range Transboundary Air Pollution (CLRTAP) approach has been used to calculate nitrogen fluxes in the energy and transport sectors. Air pollutants arise from energy production, mainly from the...
Impact of climate change on nitric oxide and nitrous oxide emission
The impact of soil type, land use and climate on emission rates of nitric oxide (NO), a precursor of atmospheric ozone (O3), andN2O, a powerful GHG, as well as ratios of N2O:NO are still not well understood in both...
Oxygen regulates nitrous production directly in agricultural soils
Soil oxygen is the key proximal factor simultaneously controlling nitrification and denitrification at the cellurar-level, and further determining the partitioning of the end products between dinitrogen and nitrous...
Nitrous oxide emissions from Soddy podzolicsandy loam soil
Site specific estimates of direct soil N2O emissions are very uncertain with soil water- filled pore space, temperature and mineral nitrogen content usually being the main controlling factors. Variations in...
The global distribution of soil nitrification
Nitrification is a major pathway of N2O production in aerobic soils. Robust prediction of gross nitrification rate (𝑅𝑛𝑖𝑡) and associated N2O production is difficult due to uncertainty in existingprocess-based...
An open-path quantum cascade laser based ammonia analyzer
Ammonia (NH3). Fertilization and livestock are the main anthropogenic sources. Concentration consumption. It is an ideal tool for NH3 flux measurements based on the eddy covariance (EC) technique in the...
Dominant contribution of nitrogen compounds in precipitation
Characterize the rain chemistry in the Lake Victoria basin, focusing on nitrogen compounds, taking into account the DissolvedOrganic Nitrogen (DON) part. In Africa, nitrogen (N) deposition to ecosystems will...
High-resolution ammonia emission Inventory in Belarus
Overview Necessity of the high-resolution ammonia emissions: air pollution and impact modeling air pollution hotspots determination development of emission reduction measures based on scientific knowledge.
Validation of nitrogen dry deposition modelling above forest
Accurate modeling of nitrogen (N) deposition is essential for identifying exceedances of N and defining critical values in environmental protection guidelines. However, there are still uncertainties in modern...
Long-term atmospheric inorganic nitrogen deposition in West African savanna
Nitrogen critical loads are poorly assessed in Africa. The International Network to study Deposition and Atmospheric chemistry in Africa (INDAAF) project,operational since 1995, has provided the first consistent...
6a. Closing the N cycle innovations for sustainable N management
Alternative fertilizers from nutrient-rich wastes for organic crops
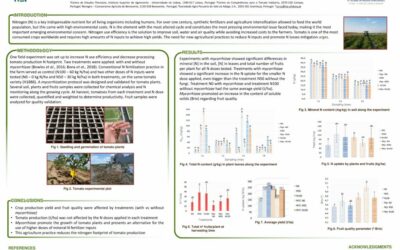
A main challenge in optimizing organic crop production is the need to acquire alternative source of nutrients to satisfy the growing demand, and to reduce the conventional manure importation. In parallel, the...
Ammonium volatilization from urea and its inhibition by urease inhibitor Limus
Invisible contribution – visible success: The addition of urease inhibitors (UI) as Limus® may reduce NH3 emissions from soil applied urea massively, thereby increasing the nitrogen use efficiency of urea-based...
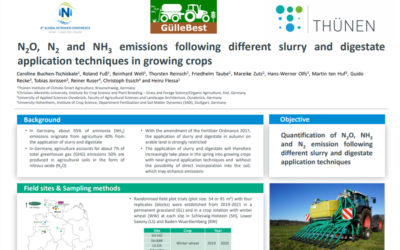
N2O, N2 and NH3 emissions following different slurry and digestate application techniques
In Germany, about 95% of ammonia (NH3) emissions originate from agriculture 40% from the application of slurry and digestate. In Germany, agriculture accounts for about 7% of total greenhouse gas (GHG)...
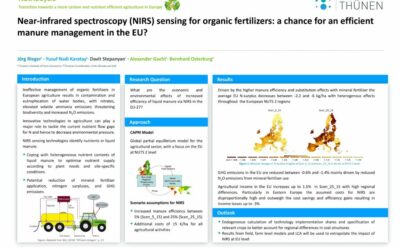
Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) sensing for organic fertilizers
Ineffective management of organic fertilizers in European agriculture results in contamination and eutrophication of water bodies, with nitrates, elevated volatile ammonia emissions threatening biodiversity and...
Sensor technologies for detection of urine patches in livestock-grazed pastures
Urine patches in grazed pastures arehotspots for nitrogen (N) losses through leaching and nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions. A New Zealand designed ground-based sensing machine, Spikey®, can detect urine patches...
Development of biodegradable polymers
Higher fertilizer use efficiency. Better alignment of nutrient release. Development of a biodegradable polymer coating for organic fertilizers. Release is slowed down by applied polymer coating ...
Liquid Swine Manure Nitrogen Conservation and Concentration Technology
An inhouse acidification system was installed to treat swine waste from one half of a 1,200 head finishing barn with a separating scraper to apply a 50% citric acid solution to a pH of 5.5 or pH 4.5 in the liquid waste...
Detection of nitrogen in winter wheat based on Sentinel-2 data
Since nitrogen is one of the most essential elements for plant nutrition, nitrogen shortage can affect crop productivity. Excess nitrogen application harms on plant health and environmental situation. Therefore,...
7a. From Science to Policy
Cost curves for ammonia mitigation measures in German livestock systems
The research work reported here is aiming at a consistent cost calculation model for livestock farming in Germany, which can be used for the exante and exposed calculation of ammonia mitigation costs. By...
Challenges facing N-regulation in Germany, The Netherlands and Denmark
EU countries are facing requirements linked to both the Water Framework Directive (WFD) and the National Emission Ceiling Directive (NEC). The work has been going on for years but there are still major challenges....
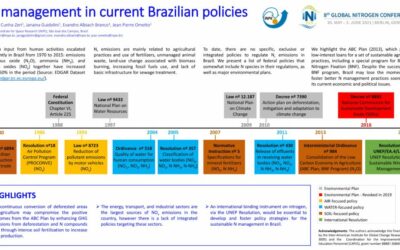
Nr management in current Brazilian policies
Nitrogen input from human activities escalated significantly in Brazil from 1970 to 2015: emissions of nitrous oxide (N2O), ammonia (NH3), andnitrogen oxides (NOx) together have increased about 350% in the period....
7b. Educational aspects, public awareness, risk communication
Communicating consequences of excess nitrogen – Short films for social media linking nitrogen and sustainable development goals
A good communication of complex environmental problems is essential to make a change. This communication should not only focus on policy makers,but also on citizens, as they are central for transformation processes.The...
Citizen dialogue on policy instruments for the reduction of reactive nitrogen in Germany
The introduction into the topic of reactive nitrogen and the collection of ideas for mitigation was focus in the regional conferences. From every regional conference six volunteers were seent to the conference of...
Measures and scenarios for the implementation of the reduction targets set by the new NEC directive
Emission reduction targets according to the NEC directive (directive (EU) 2016/2284) for NH3 (relative to 2005): 5% and 29% in 2020 and 2030, respectively (≙ 594 kt NH3 in 2020 and ≙ 444 kt NH3 in 2030) and limitation...
Special Session on Nitrogen Footprint
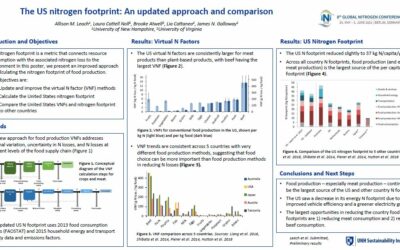
The US nitrogen footprint: An updated approach and comparison
The nitrogen footprint is a metric that connects resourceconsumption with the associated nitrogen loss to theenvironment In this poster, we present an improved approach for calculating the nitrogen footprint of food...
Indonesian nitrogen footprint assessment of food sector
Indonesia is the 4th most populated country inthe world, and it is predicted to be. The demand of food in Indonesia is high because Indonesia is populated and agrarian country. 86.4% of farmers in...
The Portuguese nitrogen footprint, a challenge in a Mediterranean country
A nitrogen (N) footprint quantifies and connects N losses with consumption patterns. This concept emerged out of the necessity to communicate the importance and the negative effects of N to the general public (N-Print,...
Nitrogen footprint calculator for Germany
Tools to calculate personal footprints can help assess and communicate the impact of lifestyle and consumption choices to individuals. In comparison to carbon footprints however, nitrogen footprints are less well-known...
A nitrogen footprint perspective for Brazilian water sector
Water management in Brazil, established nationally by law only in 1997, is based on meeting multiple water use and watershed management for “ensure current and future generations the necessary availability of water, in...
Reducing the nitrogen footprint of Portuguese wine
Nitrogen (N) is a key nutrient in crop production and crucial in vineyard management. When excessive reactive N is present in the environment, it may not only reduce crop production and increase pests and diseases...
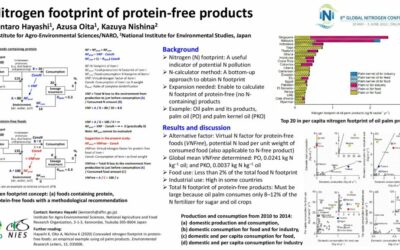
Nitrogen footprint of protein-free products
Nitrogen (N) footprint: A usefulindicator of potential N pollution. N-calculator method: A bottom-upapproach to obtain N footprint. Expansion needed: Enable to calculate N footprint of protein-free (no...
A nitrogen footprint tool (NFT) for communities
Nitrogen footprint tools (NFTs) allow entities to determine the amount of reactive nitrogen lost to the environment as a result of the entities resource use. The community NFT model estimates these loses for census...